In a web of legal complexities, the intersection of mental health and accountability raises profound questions about responsibility and the consequences of harm. Join us as we delve into the intriguing topic of Tort Liability in Cases of Insanity, where the legal system grapples with the delicate balance between justice and compassion.
The interplay between mental illness and legal culpability poses significant challenges for the justice system. On the one hand, we recognize the need to hold individuals accountable for their actions, while on the other hand, we must consider the mitigating factors of mental health conditions that may impair a person’s capacity to make rational decisions.
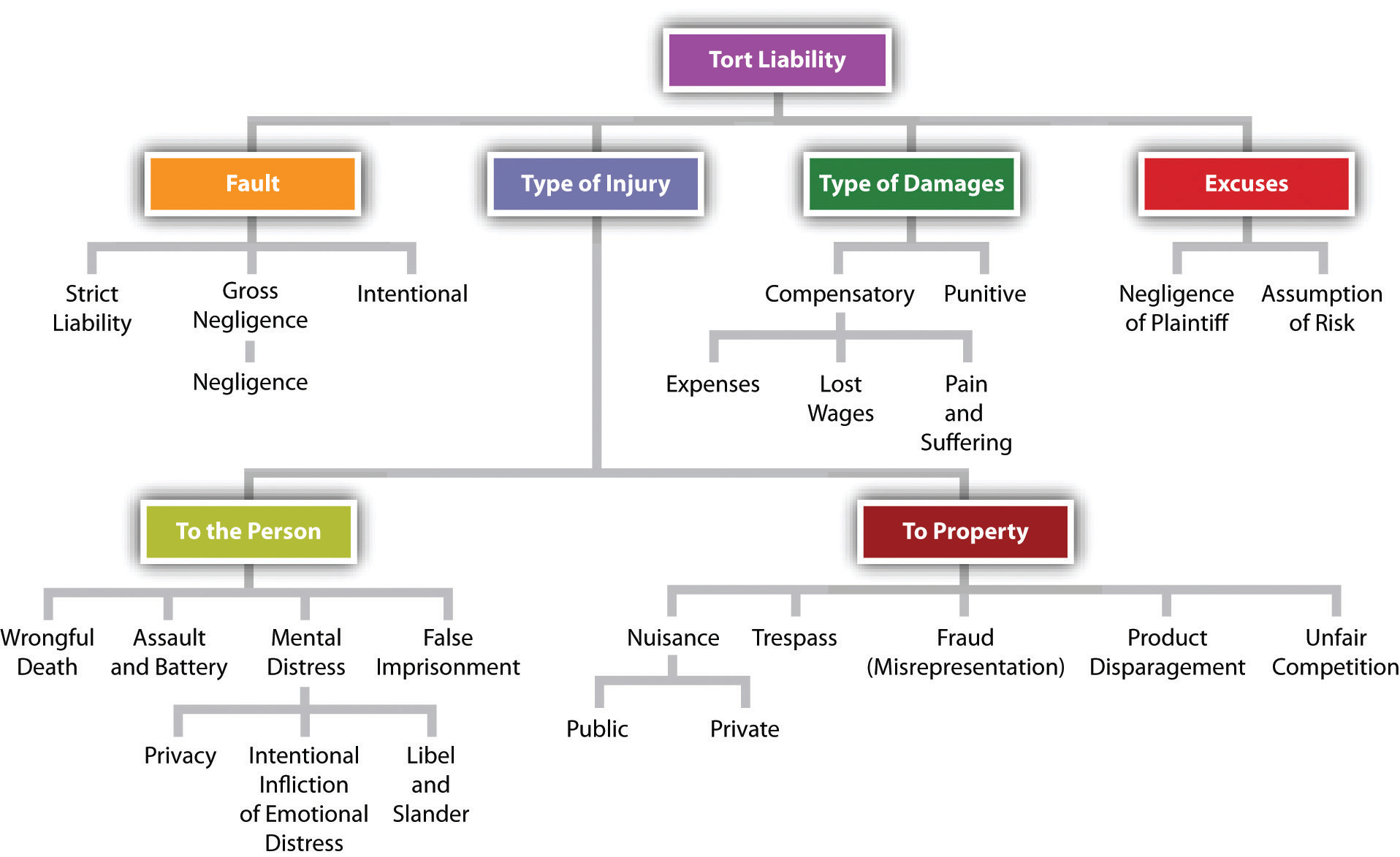
Tort law provides a framework for civil liability in cases of harm caused by the wrongful acts of others. However, in cases involving individuals with mental illness, the traditional principles of tort liability may not always be straightforward.
The legal standard for insanity in tort cases varies across jurisdictions, but generally involves assessing whether the individual lacked the mental capacity to understand the nature and consequences of their actions at the time of the alleged wrongdoing. Proving insanity can be a complex and challenging task, requiring expert psychiatric testimony and careful consideration of the individual’s mental state.
The Personal Toll of Tort Liability in Cases of Insanity
The legal ramifications of tort liability in cases of insanity can have devastating consequences for both the victims of harm and the individuals with mental illness. Victims may face challenges in obtaining compensation for their injuries, while the individuals with mental illness may face financial burdens and the stigma associated with legal proceedings.
Beyond the legal implications, tort liability can also take a toll on the mental health of the individuals involved. The stress and uncertainty of legal proceedings can exacerbate existing mental health conditions, creating a vicious cycle of distress.

Historical Perspectives on Insanity and Tort Liability
The concept of insanity as a defense in tort cases has a long and complex history. In the early days of common law, individuals with mental illness were often considered incapable of forming the necessary intent to commit a tort.
However, over time, the legal definition of insanity has evolved, reflecting changing societal attitudes and scientific understandings of mental health. Today, the insanity defense is typically based on the concept of diminished capacity, which recognizes that mental illness can impair an individual’s ability to control their behavior.

Unveiling the Hidden Truths of Tort Liability in Insanity Cases
Behind the legal complexities of tort liability in insanity cases lies a deeper exploration of human vulnerability and resilience. These cases often involve individuals who are struggling with severe mental health challenges, and it is essential to approach them with empathy and understanding.
By examining the personal experiences of those affected by tort liability in insanity cases, we can shed light on the intricate interplay between mental health and legal responsibility. It is through these stories that we can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities of human nature and the challenges faced by both victims and individuals with mental illness.
Navigating the Legal Landscape with Tort Liability in Insanity Cases
Navigating the legal landscape in tort liability cases involving insanity requires a comprehensive understanding of the relevant laws and procedures. It is essential to consult with experienced legal professionals who can provide guidance and representation throughout the process.
The insanity defense is a complex and often misunderstood aspect of tort law. By staying informed about the legal framework and seeking professional legal advice, individuals can ensure that their rights are protected and that justice is served.

Tort Liability in Insanity Cases: Beyond Legal Definitions
Beyond the legal definitions and technicalities, tort liability in insanity cases raises fundamental questions about the nature of responsibility and the role of society in addressing mental health issues.
Exploring these cases through the lens of ethics and social justice can lead to a deeper understanding of the challenges faced by individuals with mental illness and the need for a compassionate and restorative approach to justice.
Fun Facts About Tort Liability and Insanity
1. The first recorded insanity defense in English common law dates back to 1390.
2. The M’Naghten Rule, a widely used insanity defense test, was established in 1843 following the trial of Daniel M’Naghten, who assassinated the British Prime Minister at the time.
3. The American Law Institute’s Model Penal Code defines insanity as a “mental disease or defect that renders a person unable to appreciate the criminality of his conduct or to conform his conduct to the requirements of law.”

The Intersection of Tort Liability and Mental Health: A Guide
Understanding the intersection of tort liability and mental health requires a comprehensive approach that encompasses legal knowledge, psychological insights, and social context.
This guide provides a roadmap for navigating the complexities of tort liability in cases of insanity, offering practical advice and expert perspectives to help individuals make informed decisions and protect their rights.
Questions and Answers About Tort Liability in Insanity Cases
Q: Can individuals with mental illness be held legally liable for their actions?
A: In some cases, yes. If an individual with mental illness is found to have the capacity to understand the nature and consequences of their actions, they may be held legally liable for their wrongful conduct.
Q: What is the most common insanity defense used in tort cases?
A: The most common insanity defense is the M’Naghten Rule, which requires proof that the individual lacked the capacity to understand the nature and consequences of their actions due to a mental disease or defect.
Q: How is the insanity defense evaluated in court?
A: The insanity defense is typically evaluated by expert psychiatric testimony and a review of the individual’s mental state at the time of the alleged wrongdoing.

Q: What are the potential consequences of a successful insanity defense?
A: A successful insanity defense may result in the individual being found not guilty by reason of insanity, which can lead to treatment in a mental health facility rather than imprisonment.
Conclusion of Tort Liability In Cases Of Insanity: The Intersection Of Mental Health And Legal Responsibility
The intersection of tort liability and mental health presents a complex and evolving landscape that requires a compassionate and nuanced approach. By understanding the legal framework, considering the personal experiences of those involved, and engaging in meaningful discussions about ethics and social justice, we can strive for a just and equitable society that supports both victims and individuals with mental illness.
